The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that is born in the brainstem and goes all the way down the spine until the beginning of the lumbar region (L1 vertebra). It is cylindrical in shape, white in color and can measure up to 45 cm long.
At the bottom part, it has a bundle of nerves known as the horsetail and a structure called the terminal filum, which joins the spinal cord with the coccyx bone. A set of 31 spinal nerves make up the spinal cord and connect it to the rest of the body.
Functions
The spinal cord has three main functions:
- Transports information between the spinal nerves and the brain.
– Controls automatic or reflex reactions.
- Transmits nerve impulses to the muscles, blood vessels and glands through the spinal nerves.
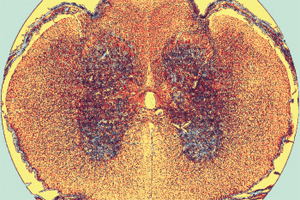
It is made up by two kinds of tissue.
- At the center is the nucleus or grew matter and it contains cell bodies as well. It is organized into four roots: two dorsal, which receive information through sensory neurons spread throughout the body, and two ventral roots, which contain the cell bodies of the motor neurons, which sent signals to the skeletal muscles.
– Surrounding the grew matter is the white matter, formed by axons of neurons that are connected in two ways: ascending, which carry incoming signals to the brain regarding physical sensations the body is feeling, and descending, which transport outgoing signals from the brain to the skeletal muscles regarding voluntary movements.







 Muere Evita
Muere Evita